Power Point for GIS Technology
تفاصيل العمل
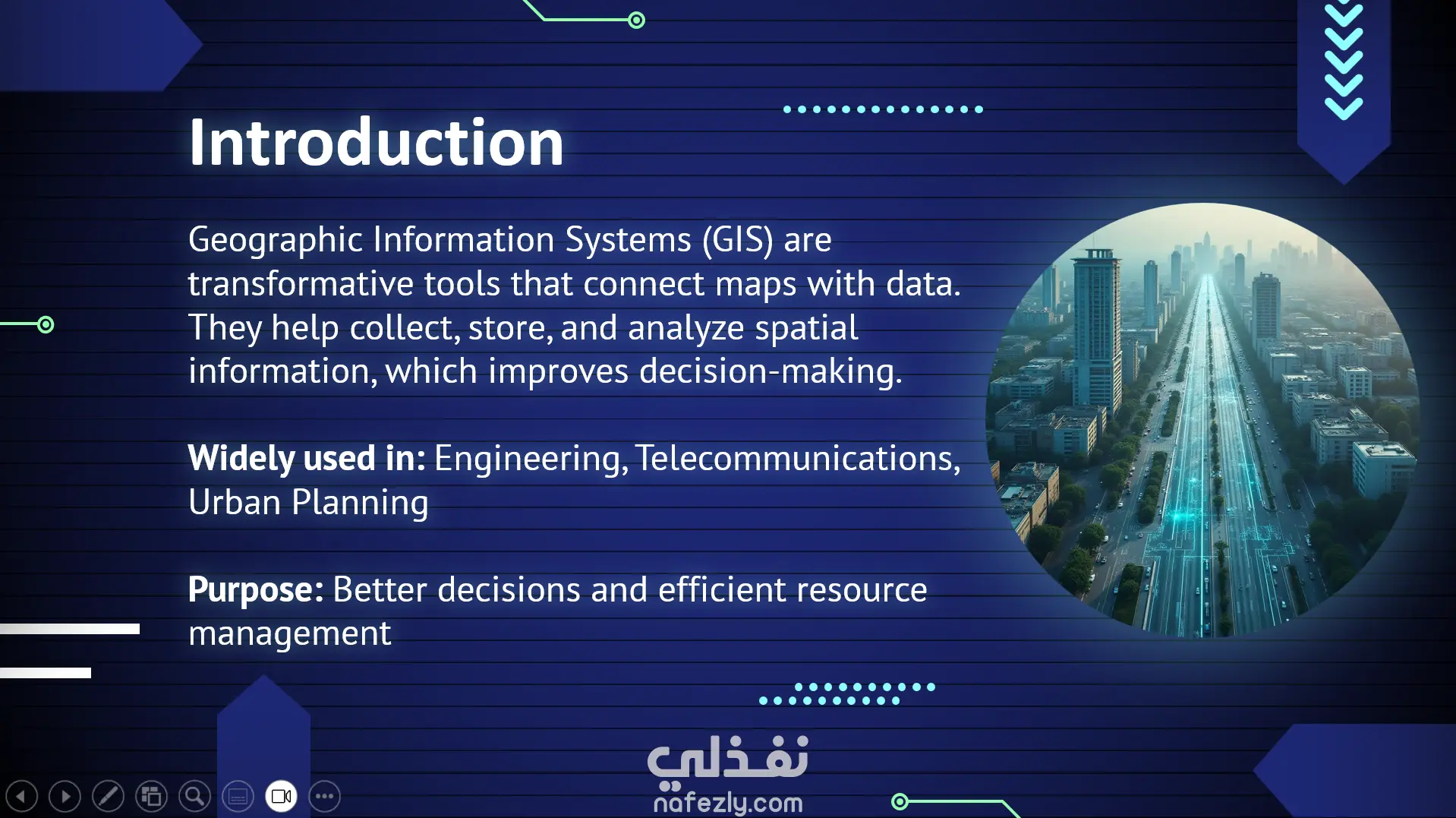
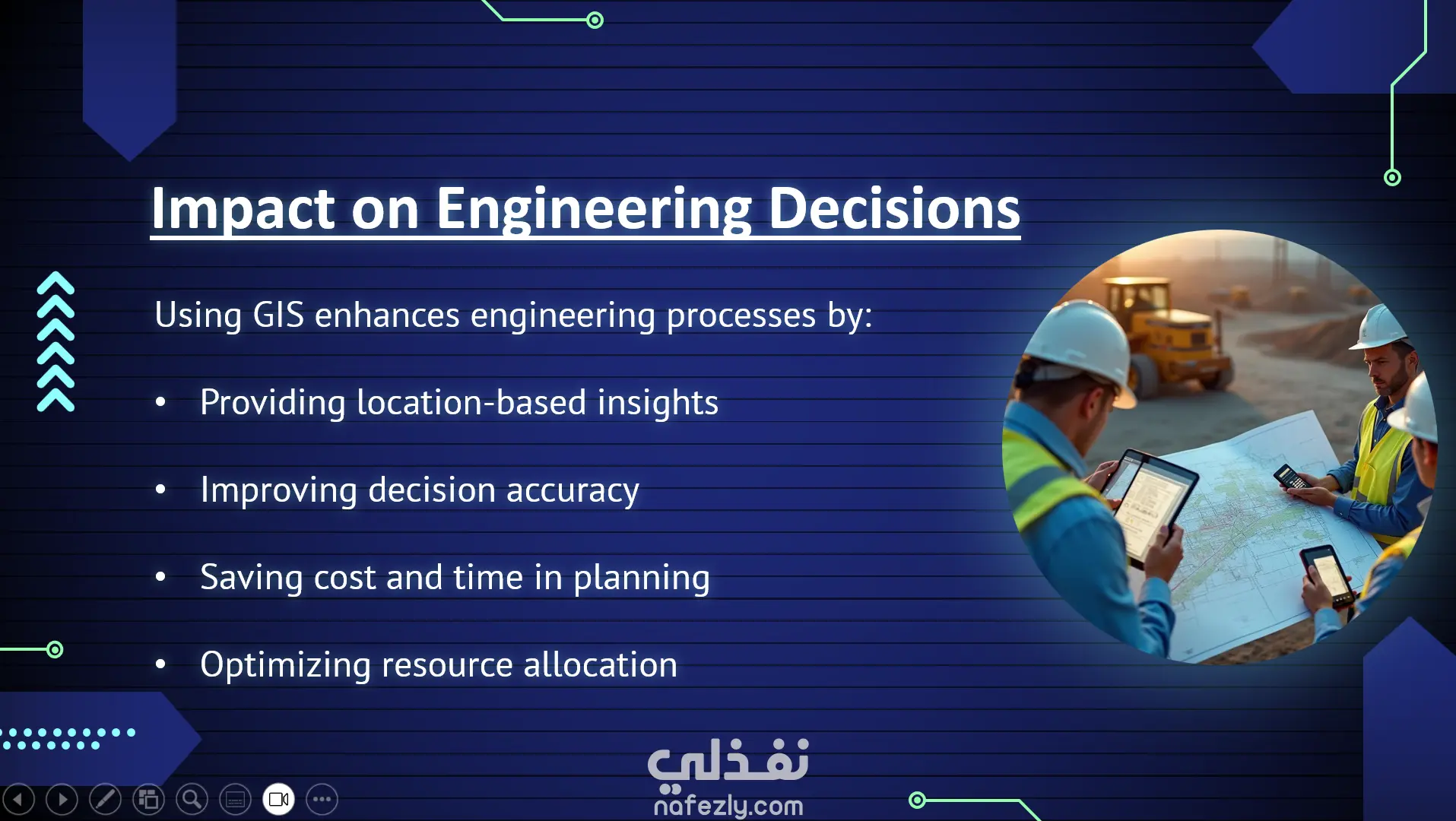
Slide 1: Title GIS Technology Geographic Information System Slide 2: Introduction Definition: A system that integrates digital maps, databases, and analysis tools. Purpose: To collect, store, analyze, and visualize spatial data. Used in: Planning, management, scientific research, and business applications. Slide 3: Components of GIS Hardware: Computers, GPS devices. Software: Programs like ArcGIS, QGIS. Data: Spatial data (maps, satellite images) and attribute data. People: Analysts, developers, decision-makers. Methods: Procedures for analyzing and managing data. Slide 4: Types of Data in GIS Spatial Data: Points: Schools, hospitals. Lines: Roads, rivers. Polygons: City boundaries, farmland. Attribute Data: Descriptive information linked to each element. Slide 5: Functions of GIS Data Capture: Collecting data from surveys, satellites. Data Storage: Organizing spatial and attribute data. Data Analysis: e.g., finding the shortest path or best project location. Visualization: Displaying data on maps and charts. Slide 6: Applications of GIS Urban Planning: City design, transportation planning. Environmental Management: Monitoring environmental changes. Disaster Management: Response to natural disasters. Agriculture: Smart farming, irrigation planning. Business: Store location analysis, market research. Slide 7: Benefits of GIS Better decision-making. Linking spatial and descriptive data. Saving time and costs. Supporting scientific research. Slide 8: Challenges of GIS High cost of hardware and software. Complexity of data collection and processing. Need for trained specialists. Continuous data updating required. Slide 9: Future of GIS Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data. Use in autonomous vehicles. Enhanced real-time monitoring of events. Slide 10: Conclusion GIS is a powerful tool for connecting spatial and attribute information. It supports problem-solving in planning, management, and research. The future brings more opportunities with emerging technologies.
بطاقة العمل
طلب عمل مماثل